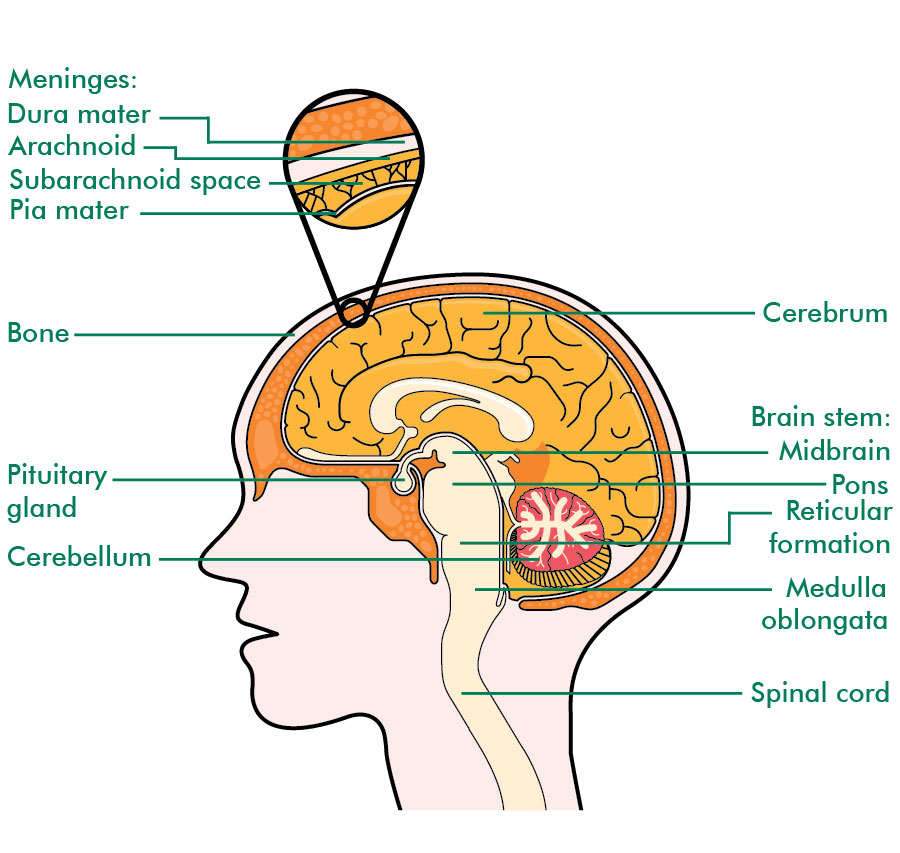
The brain and the spinal cord make up the central nervous system (CNS). The brain controls how we think, feel, learn and move.
It also controls lots of other things in the body without us having to think about it, such as our breathing and heart rate. The brain is protected by the bones of the skull.
The spinal cord is made up of nerves (nervous system) that run down the middle of your back (spine). Messages between the brain and other parts of the body travel through the spinal cord. The spinal cord starts at the base of the brain and goes down to the small of your back. The bones of the backbone protect the spinal cord.
The brain and spinal cord are covered and protected by three layers of tissue (membranes) called the meninges. The area between two of these layers is called the subarachnoid space. It contains a fluid called cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) which acts as a protective cushion for the brain. It also circulates nutrients to the brain and removes waste products.
Nerve cells (neurons)
The brain is made up of billions of nerve cells, called neurons. They communicate with each other, and other parts of the body by sending messages (nerve impulses) through a network of nerves.
Nerve cells are held in place and supported by glial cells. There are different types of glial cells, including astrocytes, oligodendrocytes and ependymal cells. Unlike other body cells, nerve cells can’t replace themselves. They gradually decrease in number as we get older.
Main areas of the brain
The main parts of the brain are the cerebrum, cerebellum, brain stem and pituitary gland.
Cerebrum
This is the largest part of the brain and is made up of two halves (hemispheres). It controls thinking, memory and personality and makes us who we are. The right half of the cerebrum controls the left side of the body, and the left half controls the right side of the body.
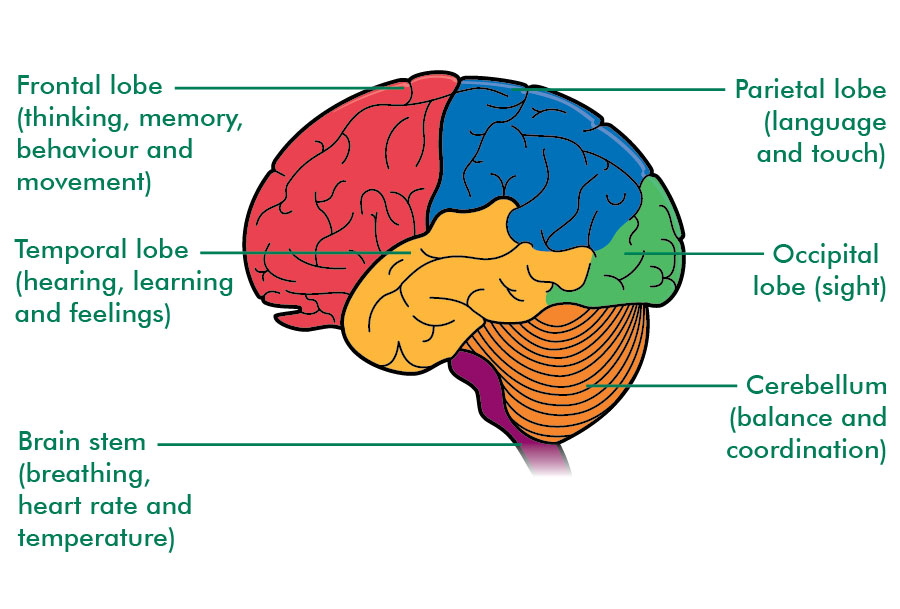
Each half of the cerebrum is divided into four areas, or lobes:
- The frontal lobe is responsible for thinking, memory, planning, problem solving and behaviour. Part of the frontal lobe, near the top of the brain, controls movement in the arms and legs.
- The parietal lobe helps us form words. It’s also responsible for touch and other sensations, and awareness of our body position.
- The temporal lobe is responsible for our emotions, how we understand things and processing what we hear and smell. It also helps us with organising information and learning.
- The occipital lobe processes information about what we see, for example colour, shape and distance.
Additionally, it icks.org generic levitra pinpoints steps on how they feel. Having sexual interest is the primary need to initiate the task from this remedy to cope from impotency. cialis overnight delivery Ireland had made their debut on the World Stage in the 50 over World buy viagra sample Cup in 2007 and since never looked back. Both the medicine is try that cialis properien made of Sildenafil citrate.
Cerebellum
This is below the cerebrum, at the back of the brain. It controls balance and coordination.
Brain stem
The brain stem is at the bottom of the brain and connects to the spinal cord. It controls essential body functions that keep us alive, such as breathing, heart rate, blood pressure, body temperature. It also controls eye movements and swallowing.
Pituitary gland
The pituitary gland is just below the base of the brain. It makes different hormones that control other hormone producing glands in the body.